Trong bài viết này, hãy cùng mình tìm hiểu về tệp KubeConfig, một trong những cách quản lý quyền truy cập người dùng.
Xem thêm:
1. Vì sao cần sử dụng KubeConfig
Sử dụng lệnh curl với certificate và key để tương tác với API Kubernetes rất phức tạp. Việc chỉ định thủ công địa chỉ máy chủ, certificate và key cho mỗi lệnh kubectl rất mất thời gian.
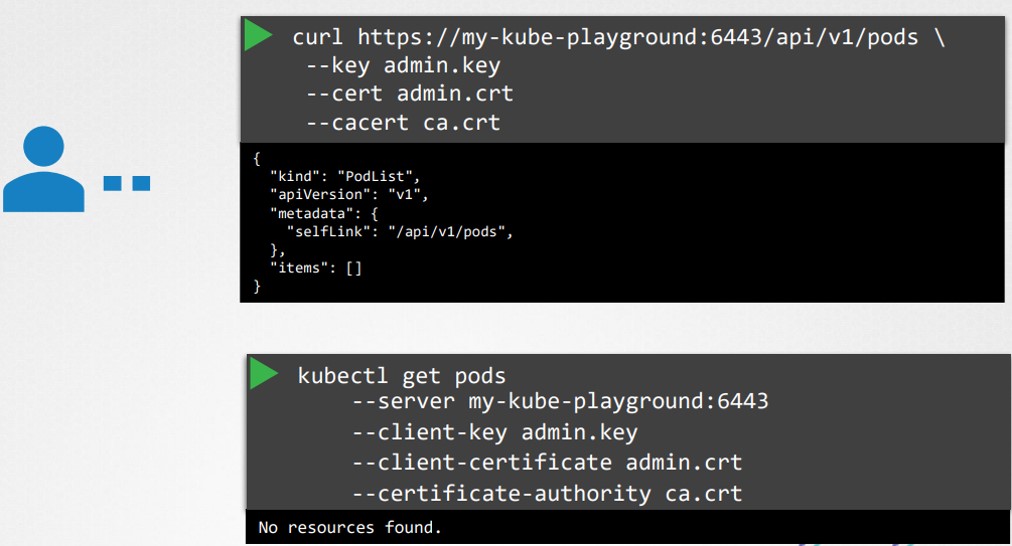
Vì vậy, KubeConfig ra đời như một giải pháp để giải quyết vấn đề này:
- Kubeconfig là một tệp cấu hình lưu trữ thông tin cần thiết để tương tác với cụm Kubernetes.
- Nó xác định các cluster, user và contexts, cho phép chuyển đổi dễ dàng giữa các môi trường và người dùng.
- Theo mặc định, kubectl tìm kiếm tệp config trong thư mục .kube dưới thư mục gốc của người dùng.
2. Cấu trúc của tệp Kubeconfig
Tệp tuân theo định dạng YAML với ba phần chính:
- Cluster: Liệt kê các cụm Kubernetes khác nhau có thể truy cập.
- User: Xác định các tài khoản người dùng với quyền truy cập vào các cluster.
- Contexts: Liên kết các cụm và người dùng, cho phép bạn xác định người dùng nào sẽ truy cập cụm nào.
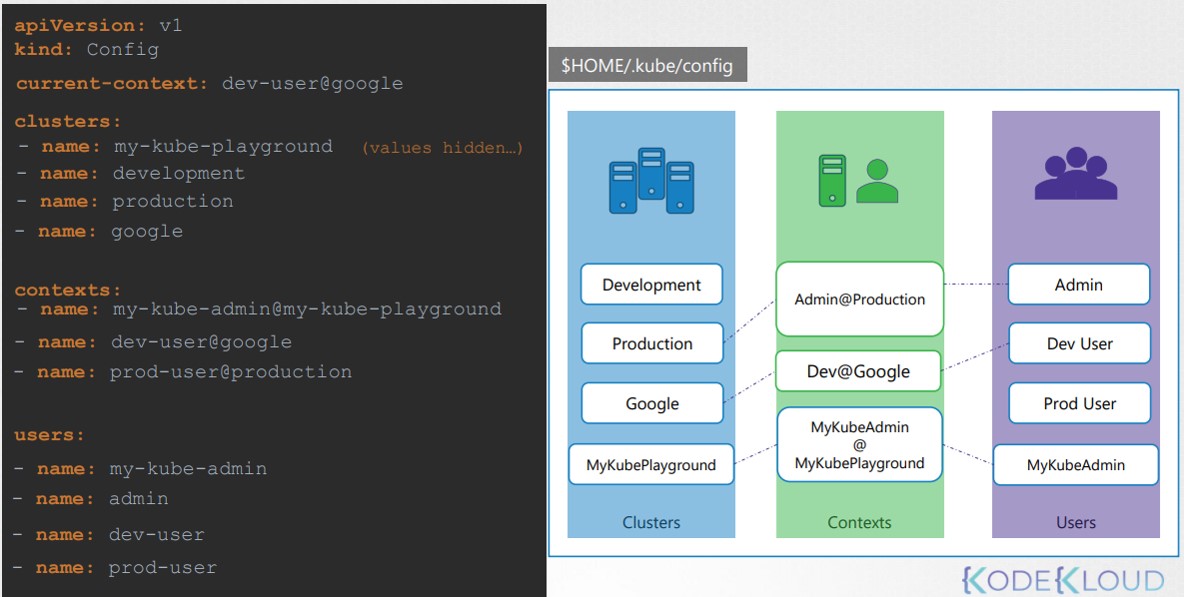
3. Một số ví dụ về KubeConfig
1. Where is the default kubeconfig file located in the current environment?
/root/.kube/config
2. How many clusters are defined in the default kubeconfig file?
controlplane ~ ➜ kubectl config view
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: DATA+OMITTED
server: https://controlplane:6443
name: kubernetes
contexts:
- context:
cluster: kubernetes
user: kubernetes-admin
name: kubernetes-admin@kubernetes
current-context: kubernetes-admin@kubernetes
kind: Config
preferences: {}
users:
- name: kubernetes-admin
user:
client-certificate-data: DATA+OMITTED
client-key-data: DATA+OMITTED
3. A new kubeconfig file named my-kube-config is created. It is placed in the /root directory. How many clusters are defined in that kubeconfig file?
controlplane ~ ➜ kubectl config view --kubeconfig my-kube-config
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority: /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
server: https://controlplane:6443
name: development
- cluster:
certificate-authority: /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
server: https://controlplane:6443
name: kubernetes-on-aws
- cluster:
certificate-authority: /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
server: https://controlplane:6443
name: production
- cluster:
certificate-authority: /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt
server: https://controlplane:6443
name: test-cluster-1
contexts:
- context:
cluster: kubernetes-on-aws
user: aws-user
name: aws-user@kubernetes-on-aws
- context:
cluster: test-cluster-1
user: dev-user
name: research
- context:
cluster: development
user: test-user
name: test-user@development
- context:
cluster: production
user: test-user
name: test-user@production
current-context: test-user@development
kind: Config
preferences: {}
users:
- name: aws-user
user:
client-certificate: /etc/kubernetes/pki/users/aws-user/aws-user.crt
client-key: /etc/kubernetes/pki/users/aws-user/aws-user.key
- name: dev-user
user:
client-certificate: /etc/kubernetes/pki/users/dev-user/developer-user.crt
client-key: /etc/kubernetes/pki/users/dev-user/dev-user.key
- name: test-user
user:
client-certificate: /etc/kubernetes/pki/users/test-user/test-user.crt
client-key: /etc/kubernetes/pki/users/test-user/test-user.key
4. I would like to use the dev-user to access test-cluster-1. Set the current context to the right one so I can do that. Once the right context is identified, use the kubectl config use-context command.
To use that context, run the command: kubectl config --kubeconfig=/root/my-kube-config use-context research
To know the current context, run the command: kubectl config --kubeconfig=/root/my-kube-config current-context
5. We don’t want to have to specify the kubeconfig file option on each command. Set the my-kube-config file as the default kubeconfig by overwriting the content of ~/.kube/config with the content of the my-kube-config file.
Replace the contents in the default kubeconfig file with the content from my-kube-config file with following command.
cp my-kube-config ~/.kube/config
6. With the current-context set to research, we are trying to access the cluster. However something seems to be wrong. Identify and fix the issue.
Try running the kubectl get pods command and look for the error. All users certificates are stored at /etc/kubernetes/pki/users.
Cảm ơn bạn đã tham khảo kubernetes cơ bản trên ttnguyen.net.